OUTCOME SPOTLIGHT
VQ-ViT Convolutional Fusion for Retinal OCT Anomaly Detection
An interpretable medical AI framework that balances diagnostic trust, accuracy, and real-world deployment efficiency.
DEMONSTRATED CAPABILITY
What This Project Achieves
This project addresses a critical challenge in medical AI: building models that are both accurate and trustworthy for real-world healthcare use. Focusing on retinal OCT imaging, the team developed an anomaly detection framework that combines explainability with computational efficiency. By integrating vision transformers, vector-quantized autoencoders, and visual saliency mapping, the project demonstrates how interpretable AI systems can support faster, more reliable clinical decision-making without sacrificing performance.
How This Was Built — Key Highlights
This project implemented a hybrid deep learning pipeline to detect and explain anomalies in retinal OCT images while maintaining fast inference performance. The approach combined representation learning, attention mechanisms, and explainability tools to balance accuracy, interpretability, and efficiency.
Developed a VQ-VAE model to capture localized retinal structures and compress image representations.
Integrated a Vision Transformer using vector-quantized tokens to model global contextual relationships.
Designed a convolutional fusion module to bridge global transformer context with local VQ-VAE precision.
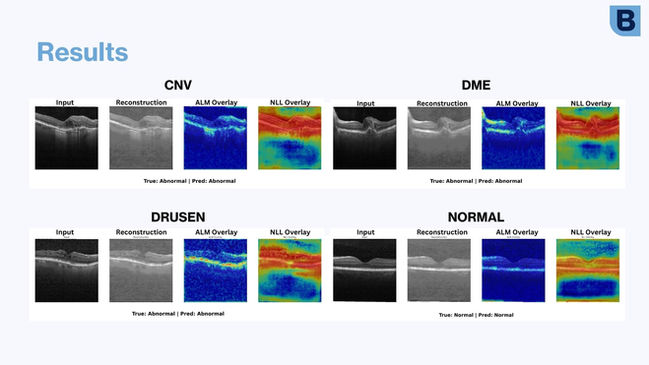
Applied Grad-CAM and Negative Log-Likelihood maps to visualize and interpret detected anomalies.
Evaluated the framework on pathological retinal conditions including Drusen, DME, and CNV.
Challenges
Building an interpretable and efficient medical AI system introduced several technical and conceptual challenges throughout the project.
Balancing model interpretability with computational efficiency required avoiding heavy autoregressive architectures.
Designing a fusion mechanism that preserved both global and local information demanded careful architectural choices.
Working with medical imaging data required understanding domain-specific pathology and imaging constraints.
Insights
Through experimentation and model analysis, the project revealed important insights about deploying AI in healthcare settings.
Interpretability is essential for clinical trust and must be designed into the model architecture rather than added post hoc.
Lightweight convolutional fusion can effectively complement transformer-based global context without excessive computation.
Combining saliency maps with probabilistic anomaly scoring improves both diagnostic confidence and transparency.
Project Gallery
Academic Team Feedback
Feedback from the Project Lead—a Senior Imaging Scientist at Novartis and researcher at MIT with extensive experience translating AI-driven medical imaging into clinical and commercial applications—highlighted the exceptional technical depth and research maturity demonstrated in this project. Drawing on his background in clinical trials, medical robotics, and retinal imaging, he noted the sophistication of the proposed VQ-ViT convolutional fusion framework, which effectively combined VQ-VAE, Vision Transformers, and saliency mapping to address complex retinal OCT anomalies such as Drusen, DME, and CNV. He further emphasized Jinhyung’s strong command of the mathematical foundations of machine learning, her ability to manage a technically demanding workflow, and her capacity to structure research progress with clarity and rigor—particularly impressive given her lack of prior applied research experience. The Academic Coordinator additionally highlighted her collaborative mindset, adaptability, and positive leadership, recognizing her contributions as central to both the project’s technical success and team cohesion.
Project Reflection
This project reshaped how I think about AI in healthcare, highlighting the importance of trust, interpretability, and efficiency alongside accuracy. It helped me bridge my computer science background with the human-centric demands of medical imaging and real-world clinical deployment.